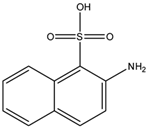
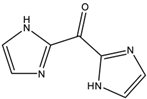
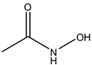
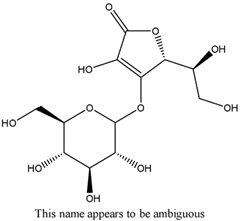
m-Tolyl acetate (PubChem CID: 67406) — also known as m-cresyl acetate, Cresatin, m-acetoxytoluene, m-cresol acetate, acetic acid m-tolyl ester, Cresatin-Sulzberger, Kresatin, acetic acid 3-methylphenyl ester, and m-methylphenyl acetate — is an aromatic ester with multiple synonymous names.